Distribution

The Future of Asset Integrity Management in Africa’s Energy Sector

Africa, the second-largest and second-most populous continent, is a region of immense potential. Its vast, untapped natural resources, coupled with a young and growing population, are driving rapid economic growth and urbanisation. As African nations push for industrialisation and electrification, energy demand is projected to more than double by 2030 and increase eightfold by 2050. This monumental shift presents both a significant opportunity and a complex challenge for the continent’s energy sector.
Historically, Africa’s energy landscape has been dominated by conventional resources—coal, natural gas, and oil—which still account for nearly 80% of its power generation. However, this reliance on fossil fuels comes with a dual dilemma: ageing infrastructure and the pressing global need to reduce carbon emissions. The International Monetary Fund’s (IMF) ‘Chart of the Month’ for April 2024 highlights Africa’s potential, identifying nine African nations among the top 20 globally with the fastest projected growth rates. This growth is attracting significant foreign investment, particularly in Sub-Saharan Africa, which is undergoing a rapid economic transformation.
The Critical Role of Asset Integrity Management
As Africa’s energy sector evolves, the management of its physical assets becomes increasingly critical. Asset Integrity Management (AIM) is a strategic framework that ensures critical infrastructure—such as pipelines, refineries, and power plants—operates reliably, safely, and efficiently throughout its lifecycle. For a continent facing the dual challenge of ageing infrastructure and ambitious growth targets, AIM is not just a best practice; it is a fundamental necessity.
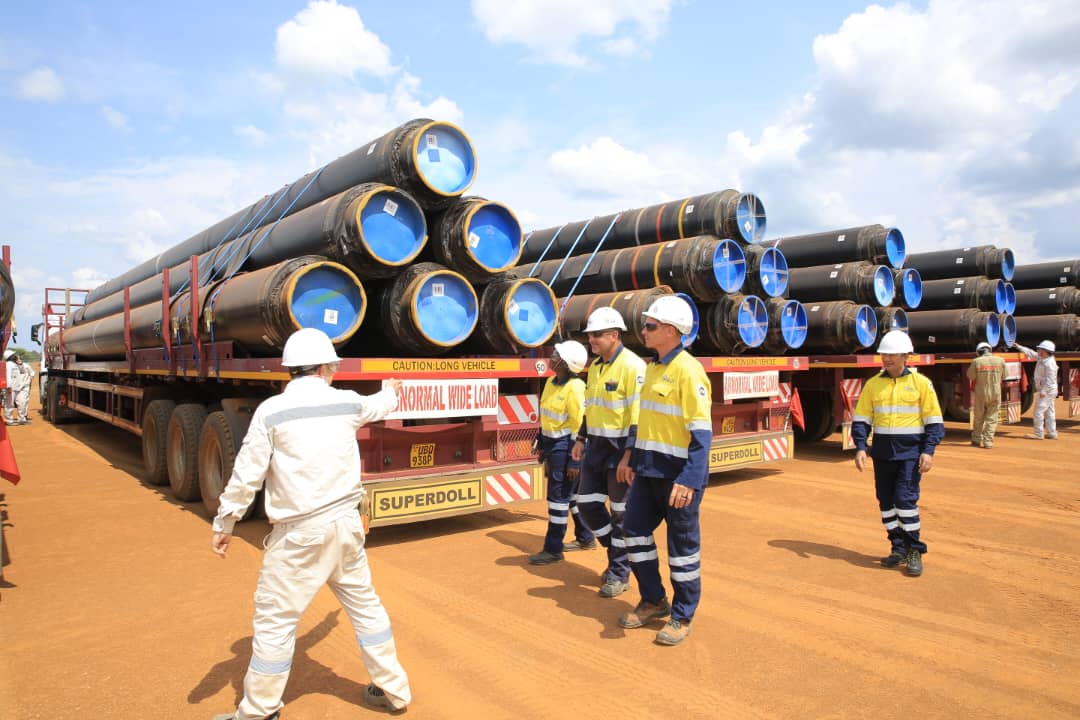
Take Nigeria as an example. As Africa’s largest oil producer and a major emerging economy, Nigeria’s energy sector is at a crossroads. Much of its infrastructure, built during past oil booms, is ageing and suffers from limited refining capacity and inefficient supply chains. These challenges result in high maintenance costs and an over-reliance on imported refined petroleum products, despite the country’s status as a major crude oil producer. A robust approach to AIM can extend the lifespan of existing assets, optimise performance, and prevent catastrophic failures, offering a sustainable path forward.
Trends Shaping the Future of Asset Integrity in Africa
The African oil and gas asset integrity market is being reshaped by several powerful trends, driving a more efficient, sustainable, and technologically advanced approach to managing energy infrastructure.
- Digitalisation and Advanced Technologies: The adoption of digital technologies is revolutionising AIM. Companies are moving beyond manual inspections to leverage predictive maintenance and real-time monitoring, enabling them to anticipate and address potential failures before they occur. Technologies such as drones for aerial inspections, IoT sensors on pipelines, and advanced data analytics provide unprecedented insights into asset health. This shift from reactive to proactive maintenance significantly reduces downtime, enhances safety, and lowers operational costs.
- Sustainability and Environmental Stewardship: With global pressure to transition to a green economy, African nations are prioritising environmental sustainability. This has created a demand for asset integrity solutions that minimise environmental impact. Companies are focusing on technologies that reduce leaks and emissions, improve waste management, and ensure compliance with stringent environmental regulations. These efforts not only meet regulatory requirements but also contribute to building a more sustainable and responsible energy sector.
- Regulatory Reforms and Policy Alignment: Across Africa, government policies are shaping the AIM landscape. For instance, Nigeria’s renewable energy policies are crucial for its energy transition but also directly impact the integrity of existing and future infrastructure. The push for cleaner energy sources and the deregulation of the oil and gas sectors create a competitive environment where operational efficiency and asset longevity are key differentiators. Policies promoting local content and partnerships further encourage companies to invest in domestic expertise and technology, fostering a self-reliant and resilient energy sector.
Adapting International Standards to Local Contexts
While international standards like ISO 9001:2015 provide a robust framework for quality management, their successful implementation in Africa requires thoughtful adaptation to local contexts. Companies with deep local knowledge are uniquely positioned to bridge this gap.
For example, NiGSA Energy Services Limited has demonstrated how global standards can be seamlessly integrated with local regulations and practices in Nigeria. By adhering to international accreditations from bodies like ABS, BV, and DNV, while also complying with local frameworks such as those from NCDMB, NiPeX, and NUPRC, NiGSA ensures its solutions are both globally competitive and locally relevant.
This approach goes beyond compliance. It involves understanding the unique challenges of the local operating environment, from logistical hurdles to workforce dynamics. By investing in human capital and transferring knowledge to Nigerians, NiGSA not only meets regulatory obligations but also contributes to the local economy and builds a skilled workforce. This dual focus on global quality and local relevance is key to sustainable success.
NiGSA Energy Services Limited: A Case Study in Excellence
Amidst the challenges of Africa’s energy sector, NiGSA Energy Services Limited has emerged as a leader in Asset Integrity Management. The company provides innovative solutions that address some of the industry’s most pressing issues, including ageing infrastructure and operational inefficiencies.
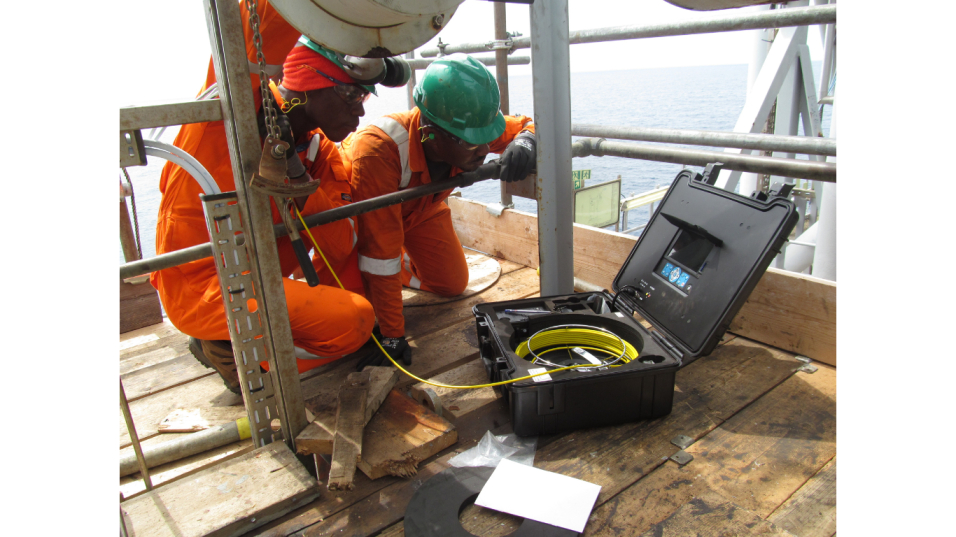
NiGSA’s comprehensive suite of services includes advanced Non-Destructive Testing (NDT), rope access for hard-to-reach areas, and cathodic protection to prevent corrosion. These services directly tackle the problem of deteriorating infrastructure, ensuring safety, reliability, and cost efficiency.
The company’s commitment to innovation and excellence has earned it multiple prestigious awards, including:
- Most Innovative Oil & Gas Servicing Company, Nigeria 2025
- Best Asset Integrity Management Company, Nigeria 2025
- Most Innovative Asset Management Solutions Provider, Nigeria 2025
NiGSA’s success is built on three key pillars:
- Advanced Technology and Strategic Partnerships: By partnering with top-tier manufacturers, NiGSA offers cutting-edge technologies and eco-friendly solutions. For example, its use of advanced NDT equipment allows for the detection of flaws in critical components without causing damage, ensuring asset longevity and safety.
- Client-Centric and Locally Adapted Solutions: NiGSA tailors its services to meet the specific needs of each client while ensuring compliance with both local and international standards. This combination of local expertise and a global outlook makes its solutions highly effective.
- Commitment to Sustainability: In line with Nigeria’s goal to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 47% by 2030, NiGSA prioritises eco-friendly solutions that improve the efficiency and lifespan of existing infrastructure, reducing the environmental footprint of oil and gas operations.
Even as major International Oil Companies (IOCs) like Shell and ExxonMobil divest from onshore operations, they remain key players in Africa’s energy sector. Their investments, along with those from TotalEnergies and Chevron, are critical. However, the success of these ventures depends on a robust AIM framework. By partnering with local experts like NiGSA, both IOCs and local companies can ensure their assets are well-maintained, their operations are efficient, and their investments are protected.
Conclusion
Africa’s energy sector stands at a pivotal moment, with immense opportunities and significant challenges ahead. Asset Integrity Management is not just a technical necessity but a strategic imperative for ensuring the safety, efficiency, and sustainability of the continent’s energy infrastructure.
By embracing digitalisation, prioritising sustainability, and fostering collaboration between international and local stakeholders, Africa can build a resilient energy sector that meets the demands of its growing population while contributing to global environmental goals. Companies like NiGSA Energy Services Limited exemplify how innovation, local expertise, and a commitment to excellence can drive this transformation.
Africa’s energy future depends on strategic collaboration, forward-thinking planning, and an unwavering commitment to asset integrity. By adopting these principles, other nations and companies across the continent can replicate this success and help build a sustainable energy landscape for generations to come.